INTRODUCTION
Kyoto Protocol
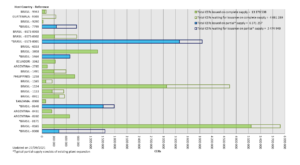
The Kyoto Protocol is an international treaty on global warming. It came into force in 2005 in the ambit of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCCC). The protocol codifies a Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) for the creation of projects in developing countries which produce environmental benefits in terms of reduction of the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. At the same time, Certified Emission Reductions (CER) are generated for the promoters of such projects. The environmental benefit for landfills is measured by reference to the lack of release into the atmosphere of the methane contained in the biogas produced by the stacked waste. The amount of methane not released into the atmosphere is converted into equivalent tonnes of CO2, as defined by the CDMs, and these are exchanged internationally in a market where the supply (by the generators of CERs) meets the demand (from those needing CERs to diminish their atmospheric emissions).